# 二叉树
# 二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历
先序:任何子树的处理顺序都是,先头节点、再左子树、然后右子树
中序:任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树、再头节点、然后右子树
后序:任何子树的处理顺序都是,先左子树、再右子树、然后头节点
# 递归方式实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历
理解递归序
每个节点都会经历3次,初次进来我,左返回我,右返回我,
// 先序-每一颗子树进来,都先打印头,再打印左,最后右,头→左→右 public static void pre(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } System.out.println(head.value); pre(head.left); pre(head.right); } // 中序-每一颗子树进来,都先打印左,再打印头,最后右,左→头→右 public static void in(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } in(head.left); System.out.println(head.value); in(head.right); } // 后序-每一颗子树进来,都先打印左,再打印右,最后头,左→右→头 public static void pos(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } pos(head.left); pos(head.right); System.out.println(head.value); }先序、中序、后序都可以在递归序的基础上加工出来
public static void f(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } // 1在这就是先序 f(head.left); // 2在这就是中序 f(head.right); // 3在这就是后序 }
第一次到达一个节点就打印就是先序、第二次打印即中序、第三次即后序
# 二叉树递归套路
# 一,重要的思想提醒
# 不管什么情况,我就想以X为头的时候,目标怎么实现.
# 实现X目标的手段,就是向左右孩子要东西,列可能性(跟X有关时候,跟X无关时候)是最重要的.
不是漫无目的的要信息,而是要简单信息,也就是常数时间可得的数据.
# 二,高度模板化
info是模板的
process是模板的
返回值是模板的,为空时候,好设置就设置,不好设置就返回null是模板的.
默认先得到左树信息,再得到右树信息是模板的.
1)假设以X节点为头,假设可以向X左树和X右树要任何信息
2)在上一步的假设下,讨论以X为头节点的树,得到答案的可能性(最重要)
3)列出所有可能性后,确定到底需要向左树和右树要什么样的信息
4)把左树信息和右树信息求全集,就是任何一棵子树都需要返回的信息S
5)递归函数都返回S,每一棵子树都这么要求
6)写代码,在代码中考虑如何把左树的信息和右树信息整合出整棵树的信息
# X 祖先节点 交集 证明题
我知道一个树中,X存在于某处,
我知道他的先序遍历,X的位置,
我知道他的后续遍历,X的位置,
请证明先序X的左边所有∩后续X的右边所有,一定是X的祖先节点
先证明X的所有祖先,一定已经存在于这个交集里.
先序遍历,符合头左右,不管我是作为左还是右,一定先经过头节点.所以我的祖先节点,一定在我左边.
后序遍历,符合左右头,不管我是作为左还是右,一定先经过我,然后才是头节点.所以我的祖先节点,一定在我右边.
所以,这个交集中,我的祖先节点一定有,而且齐全
证明为什么只有祖先节点.X的孩子节点,有没有可能出现在这个交集中.
先序遍历先遍历头,再遍历左右,所以X的子节点,在他右侧,所以不会有.
两类.X作为左树姿态的右兄弟们.X作为右树姿态下的左兄弟们.
先序遍历头左右,右兄弟一定出现在右侧,所以左侧中不包含右兄弟,交集中也就不可能存在左树姿态的右兄弟.
后续遍历左右头,如果X作为右姿态出现,左兄弟一定出现在左边,不会出现在右边,所以,不会出现在交集中.
至此,所有情况分析完毕,交集中,只可能祖先节点出现在A∩B.
# 非递归方式实现二叉树的先序、中序、后序遍历
# 先序
先序就是头左右,也就是遍历任何一个节点时候,我们先看头节点(直接打印)有没有左,有就先打印左,然后右.
准备一个栈,将头节点,压栈,然后弹出,弹出时,先右后左压栈.做完了然后弹出,弹出一个节点,他就是头,然后重复之前的操作,右压栈,左压栈,然后弹出,直到所有节点完成.
public static void pre(Node head) {
System.out.print("pre-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.add(head);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
//弹出的时候,直接先打印自己,然后先右后左压栈,然后弹出.重复操作.
head = stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
if (head.right != null) {
stack.push(head.right);
}
if (head.left != null) {
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
# 后序
后序就是左头右,
先序我们是头左右,那我们能不能搞个头右左呢?先压左,再压右,弹出时候就是了.倒着看,是不是就是左右头了呢?
所以我们搞2个栈,一个就是搞头左右,第二个我们把弹出的压到另一个里,让他逆序.
//双栈,简单方法
public static void pos1(Node head) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (head != null) {
Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>();
Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>();
s1.push(head);
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
head = s1.pop(); // 头 右 左
s2.push(head);
if (head.left != null) {
s1.push(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
s1.push(head.right);
}
}
// 左 右 头
while (!s2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
// 单栈,复杂方法,很难,
public static void pos2(Node h) {
System.out.print("pos-order: ");
if (h != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
stack.push(h);
Node c = null;
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
c = stack.peek();
if (c.left != null && h != c.left && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.left);
} else if (c.right != null && h != c.right) {
stack.push(c.right);
} else {
System.out.print(stack.pop().value + " ");
h = c;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
# 中序
- 当前节点cur,整条左边界进栈,直到遇空,转步骤2
- 栈中元素弹出,打印,节点右孩子转为cur,转1,
- 栈空停止.
public static void in(Node cur) {
System.out.print("in-order: ");
if (cur != null) {
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
while (!stack.isEmpty() || cur != null) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = stack.pop();
System.out.print(cur.value + " ");
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
# 二叉树按层遍历
# 核心:队列.
- 头进
- 头出,弹出就打印,有左加左,有右加右.
- 一个个出队列,出的时候,执行步骤2.
public static void level(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
System.out.println(cur.value);
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
}
}
}
# 二叉树的序列化和反序列化.非常高频
就是内存里的东西持久化和加载到内存里,就叫序列化和反序列化.
重要的就是null值要找东西替代,否则分不清.
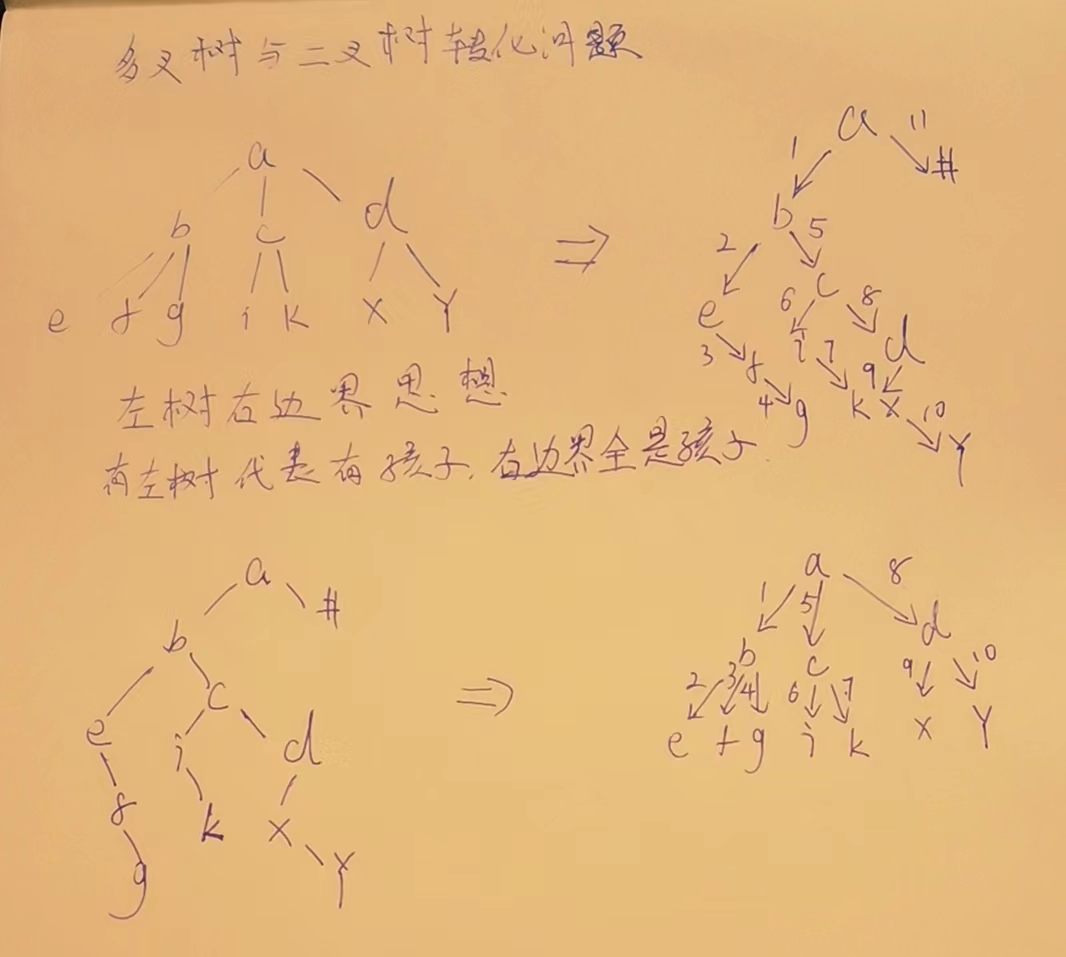
# 多叉树和二叉树的转换
一颗多叉树,如果转换为二叉树,并且可以由这个二叉树转换回来.
乐扣原题 付费题:https://leetcode.com/problems/encode-n-ary-tree-to-binary-tree
// 提交时不要提交这个类
public static class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {
}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
// 提交时不要提交这个类
public static class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) {
val = x;
}
}
// 只提交这个类即可
class Codec {
// Encodes an n-ary tree to a binary tree.
public TreeNode encode(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode head = new TreeNode(root.val);
head.left = en(root.children);
return head;
}
private TreeNode en(List<Node> children) {
TreeNode head = null;
TreeNode cur = null;
for (Node child : children) {
TreeNode tNode = new TreeNode(child.val);
if (head == null) {
head = tNode;
} else {
cur.right = tNode;
}
cur = tNode;
cur.left = en(child.children);
}
return head;
}
// Decodes your binary tree to an n-ary tree.
public Node decode(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
return new Node(root.val, de(root.left));
}
public List<Node> de(TreeNode root) {
List<Node> children = new ArrayList<>();
while (root != null) {
Node cur = new Node(root.val, de(root.left));
children.add(cur);
root = root.right;
}
return children;
}
}
# 按层遍历-非常高频
# 求二叉树最宽的层有多少节点
不一定越下面的越多.
我们可以按层遍历了,那我们是不是直到一层什么时候结束了,就知道这层有多少个了.
要想知道我这层什么时候结束,得上一层告诉我,我这层最右面的,一定是上一层的能最右的最右,不能最右的左孩子.也就是上一行最后一个节点滚的时候,我新一行开始遍历.
cur
curEnd
nextEnd
maxCount
第一行,根节点就是end了,cur = 根节点,curEnd = 根节点,nextEnd有左更新左,有右更新为右.遍历过程中,统计maxCount
当cur = curEnd时候,我们就直到当前行遍历完了,开始下一行,curEnd = nextEnd,cur=null,nextEnd=null,maxCount = 0.
public static int maxWidthNoMap(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
Node curEnd = head; // 当前层,最右节点是谁
Node nextEnd = null; // 下一层,最右节点是谁
int max = 0;
int curLevelNodes = 0; // 当前层的节点数
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.add(cur.left);
nextEnd = cur.left;
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.add(cur.right);
nextEnd = cur.right;
}
curLevelNodes++;
if (cur == curEnd) {
max = Math.max(max, curLevelNodes);
curLevelNodes = 0;
curEnd = nextEnd;
}
}
return max;
}
# 找后继节点问题
如果一个树节点,有三条指针,多了个指向父节点的指针.怎么快速找到后继节点.
后继节点就是,一个树按照中序遍历,他后面的第一个节点.
普通的方法,需要O(N),先中序遍历,然后找到x的后一个.
实际上可以做到O(k),k是x节点到后继节点的实际距离.
1.如果x有右树,那么后继节点就是右树的最左孩子.
2.如果x没有右树,往上看,只要他是父亲的右孩子,不断向上找,直到作为父亲的左孩子. 因为中序是头左右,x右树没有,说明他一直往上的头节点的右树打印完了,该回到头节点了,这个头,就是后继,如果没有头,就是没后继节点.
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
public static Node getSuccessorNode(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
if (node.right != null) {
return getLeftMost(node.right);
} else { // 无右子树
Node parent = node.parent;
while (parent != null && parent.right == node) { // 当前节点是其父亲节点右孩子
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
return parent;
}
}
public static Node getLeftMost(Node node) {
if (node == null) {
return node;
}
while (node.left != null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
# 二叉树折纸问题
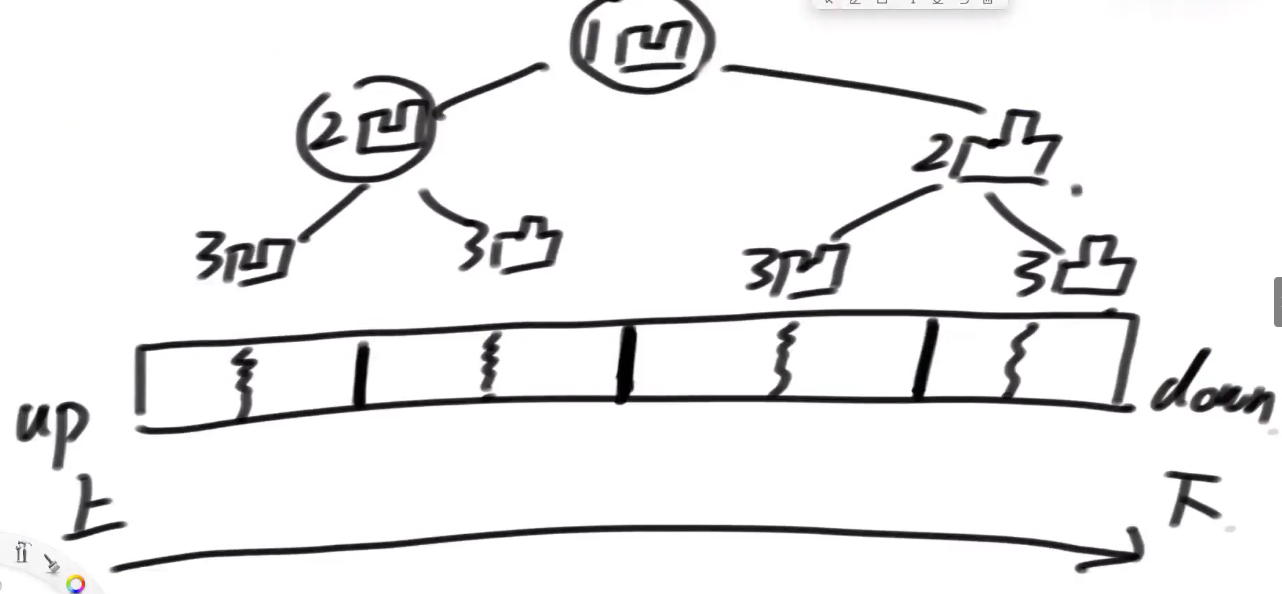
请把一段纸条竖着放在桌子上,然后从纸条的下边向上方对折1次,压出折痕后展开。此时折痕是凹下去的,即折痕突起的方向指向纸条的背面。 如果从纸条的下边向上方连续对折2次,压出折痕后展开,此时有三条折痕,从上到下依次是下折痕、下折痕和上折痕。 给定一个输入参数N,代表纸条都从下边向上方连续对折N次。 请从上到下打印所有折痕的方向。 例如:N=1时,打印: down N=2时,打印: down down up
实际操作折一下这个纸,发现这是一颗有明确规则的二叉树
- 头次折痕,凹.
- 左子树的头节点,都是凹
- 右子树的头节点,都是凸
public static void printAllFolds(int N) {
process(1, N, true);
System.out.println();
}
// 当前你来了一个节点,脑海中想象的!
// 这个节点在第i层,一共有N层,N固定不变的
// 这个节点如果是凹的话,down = T
// 这个节点如果是凸的话,down = F
// 函数的功能:中序打印以你想象的节点为头的整棵树!
//例如N=3,打印 凹凹凸凹凹凸凸
public static void process(int i, int N, boolean down) {
if (i > N) {
return;
}
process(i + 1, N, true);
System.out.print(down ? "凹 " : "凸 ");
process(i + 1, N, false);
}
# 判断是否完全二叉树
完全二叉树定义:要么是满的,要么是最后一行不满,即使不满,也是从左往右变满的过程.
# 普通方法遍历解法
就是一个二叉树的按层遍历,其中遵循一些规则,如果不遵循规则了,则不是.
- 有右没有左.肯定不是了
- 第一次遇到2个孩子不满的情况.剩下遍历节点必须是叶子节点
public static boolean isCBT1(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 是否遇到过左右两个孩子不双全的节点
boolean leaf = false;
Node l = null;
Node r = null;
queue.add(head);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
head = queue.poll();
l = head.left;
r = head.right;
if (
// 如果遇到了不双全的节点之后,又发现当前节点不是叶节点
(leaf && (l != null || r != null))
||
//有右无左
(l == null && r != null)
) {
return false;
}
//这些就是二叉树按层遍历需要的,没什么好说的
if (l != null) {
queue.add(l);
}
if (r != null) {
queue.add(r);
}
if (l == null || r == null) {
leaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
# 二叉树递归套路解法
列可能性:
如果X为头,只要满足这4个条件,那么任何一个子树,就是完全二叉树.包括树整体.
- 左树满,右树满,且高度一样,那肯定是完全二叉树
- 左树是完全,右树是满的,左树高度比右树高度高1
- 左树是满的,右树也是满的,左树高度比右树高1
- 左树是满的,右树是完全,且左右高度一样.
所以,我们的info需要,是不是满的isFull,是不是完全isCBT,高度height
public static boolean isCBT2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
return process(head).isCBT;
}
// 对每一棵子树,是否是满二叉树、是否是完全二叉树、高度
public static class Info {
public boolean isFull;
public boolean isCBT;
public int height;
public Info(boolean full, boolean cbt, int h) {
isFull = full;
isCBT = cbt;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node X) {
//为空好设置的,是满的,是完全,高度0
if (X == null) {
return new Info(true, true, 0);
}
Info leftInfo = process(X.left);
Info rightInfo = process(X.right);
//高度就是左右高度+自己
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1;
//判断是否是满的
boolean isFull = leftInfo.isFull
&&
rightInfo.isFull
&& leftInfo.height == rightInfo.height;
//判断是否是完全
boolean isCBT = false;
if (isFull) {
isCBT = true;
} else { // 以x为头整棵树,不满
if (leftInfo.isCBT && rightInfo.isCBT) {
if (leftInfo.isCBT
&& rightInfo.isFull
&& leftInfo.height == rightInfo.height + 1) {
isCBT = true;
}
if (leftInfo.isFull
&&
rightInfo.isFull
&& leftInfo.height == rightInfo.height + 1) {
isCBT = true;
}
if (leftInfo.isFull
&& rightInfo.isCBT && leftInfo.height == rightInfo.height) {
isCBT = true;
}
}
}
return new Info(isFull, isCBT, height);
}
# 判断是否为平衡二叉树
每一颗子树,左右孩子高度差不超过1. 注意是每一颗子树.
怎么就说他是了呢,列可能性,x节点作为头的情况下
- 左树是平衡二叉树
- 右树是平衡二叉树
- |x左高度-x右高度|<2
如果x从左右,都能要回信息,判断下即可.
public static boolean isBalanced2(Node head) {
return process(head).isBalanced;
}
public static class Info{
public boolean isBalanced;
public int height;
public Info(boolean i, int h) {
isBalanced = i;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
if(x == null) {
return new Info(true, 0);
}
//获取左右树信息,
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
//如果违反了,把标志改为false
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1;
boolean isBalanced = true;
if(!leftInfo.isBalanced) {
isBalanced = false;
}
if(!rightInfo.isBalanced) {
isBalanced = false;
}
if(Math.abs(leftInfo.height - rightInfo.height) > 1) {
isBalanced = false;
}
return new Info(isBalanced, height);
}
# 判断是否为搜索二叉树
对于任何一个头节点,每一颗子树,左孩子都比我小,右孩子都比我大.
public static boolean isBST2(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
}
return process(head).isBST;
}
public static class Info {
public boolean isBST;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(boolean i, int ma, int mi) {
isBST = i;
max = ma;
min = mi;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
//获取左右孩子信息
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
//收集最大最小值,全都要,所有节点一视同仁.
int max = x.value;
if (leftInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(max, leftInfo.max);
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(max, rightInfo.max);
}
int min = x.value;
if (leftInfo != null) {
min = Math.min(min, leftInfo.min);
}
if (rightInfo != null) {
min = Math.min(min, rightInfo.min);
}
/**
* 出现下列情况,判断不成立
* 1.左或者右不是了,那整棵树都不是了.
* 2.左侧的不为空&&左侧最大值不比我小
* 3.右侧的不为空&&右侧的最小值不比我大
*/
boolean isBST = true;
if (leftInfo != null && !leftInfo.isBST) {
isBST = false;
}
if (rightInfo != null && !rightInfo.isBST) {
isBST = false;
}
if (leftInfo != null && leftInfo.max >= x.value) {
isBST = false;
}
if (rightInfo != null && rightInfo.min <= x.value) {
isBST = false;
}
return new Info(isBST, max, min);
}
# 返回整棵二叉树最大距离问题
给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,任何两个节点之间都存在距离, 返回整棵二叉树的最大距离
用二叉树的递归套路做
列可能性
答案与我X无关
那答案肯定是我的某个子树或者某个右树中最大,不经过我
答案与我X有关
那就我我的左树高度,经过我(+1),然后到我右树的高度.
public static int maxDistance2(Node head) {
return process(head).maxDistance;
}
public static class Info {
//如果最大距离不经过我这个头节点,那可能是这个左树或右树的最大距离
public int maxDistance;
//如果经过我这个头节点,那就是左树高度+右树高度+我的高度(+1)
public int height;
public Info(int m, int h) {
maxDistance = m;
height = h;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x) {
//x为空,好不好设置?
//好设置,就是没有嘛,最大距离是0,高度也是0.
if (x == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
//后序遍历,收集左,收集右
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
//我需要两个信息,一个不经过我时候,就是左右孩子的某个最大的距离 max(leftMaxDis,rightMaxDis)
//一个是经过我时,那我需要左右孩子的层高,再加我.
//我判断哪个更大,返回哪个.
int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1;
int p1 = leftInfo.maxDistance;
int p2 = rightInfo.maxDistance;
int p3 = leftInfo.height + rightInfo.height + 1;
int maxDistance = Math.max(Math.max(p1, p2), p3);
return new Info(maxDistance, height);
}
# 判断二叉树是不是满二叉树
就是如果高度是h,那二叉树共有2^h-1个节点.
方法一:那我就问问我的左右子树,要一个高度和节点个数,如果最后等于2^h-1个节点,那就是,否则就不是满二叉树
// 第一种方法 // 收集整棵树的高度h,和节点数n // 只有满二叉树满足 : 2 ^ h - 1 == n public static boolean isFull1(Node head) { if (head == null) { return true; } Info1 all = process1(head); return (1 << all.height) - 1 == all.nodes; } public static class Info1 { public int height; public int nodes; public Info1(int h, int n) { height = h; nodes = n; } } public static Info1 process1(Node head) { if (head == null) { return new Info1(0, 0); } Info1 leftInfo = process1(head.left); Info1 rightInfo = process1(head.right); int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1; int nodes = leftInfo.nodes + rightInfo.nodes + 1; return new Info1(height, nodes); }方法二,那我就问问我的左右子树,如果都是满的,并且高度一样,那就是,否则整体就不是满二叉树
// 第二种方法 // 收集子树是否是满二叉树 // 收集子树的高度 // 左树满 && 右树满 && 左右树高度一样 -> 整棵树是满的 public static boolean isFull2(Node head) { if (head == null) { return true; } return process2(head).isFull; } public static class Info2 { public boolean isFull; public int height; public Info2(boolean f, int h) { isFull = f; height = h; } } public static Info2 process2(Node h) { if (h == null) { return new Info2(true, 0); } Info2 leftInfo = process2(h.left); Info2 rightInfo = process2(h.right); boolean isFull = leftInfo.isFull && rightInfo.isFull && leftInfo.height == rightInfo.height; int height = Math.max(leftInfo.height, rightInfo.height) + 1; return new Info2(isFull, height); }
# 返回最大的二叉搜索子树
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-bst-subtree (opens new window)
给定一棵二叉树的头节点head, 返回这颗二叉树中最大的二叉搜索子树的大小
二叉树递归套路
跟我的左右子树要信息,
{
我的左右树最大二叉搜索子树的节点数量 maxBSTSubTreeSize.
左右树所有的节点数量 allSize
最大值 max
最小值 min
还可以通过 maxBSTSubTreeSize == allSize 判断是否整棵树是儿叉搜索子树.
}
列可能性
经过我X这个头节点,共同组成大的二叉搜索子树
- 左树得是二叉搜索子树
- 右树得是二叉搜索子树
- 左树最大值比我小 && 右树最小值比我大.
那就是左侧所有的节点+右侧所有的节点+我自己(+1)
不经过X这个头节点,左树或者右树中,有个最大儿叉搜索子树
比比左右哪个子树的更大,
1,2,取一个最大值返回即可.
需要考虑的点,如果X为空,最大最小值不好设置值啊.不好设置,所以返回null,用的时候再判断.
// 提交如下的largestBSTSubtree方法,可以直接通过
public static int largestBSTSubtree(TreeNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
return process(head).maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
public static class Info {
public int maxBSTSubtreeSize;
public int allSize;
public int max;
public int min;
public Info(int m, int a, int ma, int mi) {
maxBSTSubtreeSize = m;
allSize = a;
max = ma;
min = mi;
}
}
public static Info process(TreeNode x) {
if (x == null) {
return null;
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right);
//只有一个节点时候,我就认为他是一个二叉搜索子树,
int max = x.val;
int min = x.val;
int allSize = 1;
//有左跟左比,
if (leftInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(leftInfo.max, max);
min = Math.min(leftInfo.min, min);
allSize += leftInfo.allSize;
}
//有右跟右比,
if (rightInfo != null) {
max = Math.max(rightInfo.max, max);
min = Math.min(rightInfo.min, min);
allSize += rightInfo.allSize;
}
//不经过X的两种可能性
int p1 = -1;
if (leftInfo != null) {
p1 = leftInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
int p2 = -1;
if (rightInfo != null) {
p2 = rightInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize;
}
//经过X的可能性.
int p3 = -1;
boolean leftBST = leftInfo == null ? true : (leftInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize == leftInfo.allSize);
boolean rightBST = rightInfo == null ? true : (rightInfo.maxBSTSubtreeSize == rightInfo.allSize);
//左右都是
if (leftBST && rightBST) {
//最大最小值条件符合.
boolean leftMaxLessX = leftInfo == null ? true : (leftInfo.max < x.val);
boolean rightMinMoreX = rightInfo == null ? true : (x.val < rightInfo.min);
//收集节点数量.
if (leftMaxLessX && rightMinMoreX) {
int leftSize = leftInfo == null ? 0 : leftInfo.allSize;
int rightSize = rightInfo == null ? 0 : rightInfo.allSize;
p3 = leftSize + rightSize + 1;
}
}
return new Info(Math.max(p1, Math.max(p2, p3)), allSize, max, min);
}
# 二叉树最先公共祖先问题
给定一棵二叉树的头节点head,和另外两个节点a和b。 返回a和b的最低公共祖先
与X无关(X不是ab的汇集点){
左侧已经有答案了
右侧已经有答案了
a,b没找到,不全
}
与X有关(X本身就是答案){
左侧有1个,右侧有一个.
x本身就是ab中的一个.
}
总结需要跟孩子要的信息,是否有a,是否有b,答案(只有已经有ab的情况下才不是null)
public static Node lowestAncestor2(Node head, Node a, Node b) {
return process(head, a, b).ans;
}
public static class Info {
public boolean findA;
public boolean findB;
public Node ans;
public Info(boolean fA, boolean fB, Node an) {
findA = fA;
findB = fB;
ans = an;
}
}
public static Info process(Node x, Node a, Node b) {
//为空好设置的那种
if (x == null) {
return new Info(false, false, null);
}
Info leftInfo = process(x.left, a, b);
Info rightInfo = process(x.right, a, b);
boolean findA = (x == a) || leftInfo.findA || rightInfo.findA;
boolean findB = (x == b) || leftInfo.findB || rightInfo.findB;
Node ans = null;
//左侧有答案了,那就是左侧的答案,左侧的答案肯定更靠近最低公共祖先
if (leftInfo.ans != null) {
ans = leftInfo.ans;
//右侧有答案了,那就是右侧的答案,右侧的答案肯定更靠近最低公共祖先,左右绝对不可能同时有答案.
} else if (rightInfo.ans != null) {
ans = rightInfo.ans;
//否则,左边或者右边一边发现一个或者X就是其中一个,那我X就是最低公共祖先.不可能一边发现两个,否则会走上面2个分支.
} else if (findA && findB) {
ans = x;
}
return new Info(findA, findB, ans);
}
# 排队最大快乐值问题
派对的最大快乐值 公司的每个员工都符合 Employee 类的描述。整个公司的人员结构可以看作是一棵标准的、 没有环的多叉树。树的头节点是公司唯一的老板。除老板之外的每个员工都有唯一的直接上级。 叶节点是没有任何下属的基层员工(subordinates列表为空),除基层员工外,每个员工都有一个或多个直接下级。
如果一个节点来了,他的直接父子节点一定不能来
如果一个节点不来,他的直接父子节点可以来,也可以不来.
public static int maxHappy2(Employee head) {
Info allInfo = process(head);
return Math.max(allInfo.no, allInfo.yes);
}
public static class Info {
//当前节点不来的情况,最大值多少
public int no;
//当前节点来的情况,最大值多少
public int yes;
public Info(int n, int y) {
no = n;
yes = y;
}
}
public static Info process(Employee x) {
if (x == null) {
return new Info(0, 0);
}
int no = 0;
int yes = x.happy;
for (Employee next : x.nexts) {
Info nextInfo = process(next);
//每个子级分别收集结果
//当我X不来时候,每个子级都可以来或者不来,取个最大值.
no += Math.max(nextInfo.no, nextInfo.yes);
//当我X来的时候,每个子级一定不能来.
yes += nextInfo.no;
}
return new Info(no, yes);
}